-
Články
Reklama
- Vzdělávání
- Časopisy
Top články
Nové číslo
- Témata
Reklama- Videa
- Podcasty
Nové podcasty
Reklama- Kariéra
Doporučené pozice
Reklama- Praxe
ReklamaSynthesis and biological properties of chosen symmetrical amides and thioamides of terephthalic acid
Authors: Agnieszka Jędrzejowska 1; Marek Matussek 1; Violetta Kozik 1; Andrzej Bąk 1; Iveta Zadražilová 2; Joseph Jampílek 2
Authors place of work: University of Silesia, Institute of Chemistry, Katowice, Poland 1; University of Veterinary and Pharmaceutical Sciences, Brno, Czech Republic 2
Published in the journal: Čes. slov. Farm., 2015; 64, 296-297
Category: 44<sup>th</sup> Conference drug synthesis and analysis
Introduction
Modern Organic Chemistry is a research area which connects not only the synthesis of new chemical compounds with interesting properties, but also the design and prediction of attractive structures and properties. The new compounds are widely used in various industries such as pharmaceutical, electronics, chemical and others.
Diamides of terephthalic acid obtained in the reactions with amino acids possess interesting properties. Functionalization using bioactive compounds is attractive in terms of synthesis, as in this way it is possible to get new active analogs.
Experimental methods
The aim of this study was the synthesis of new diamide and dithioamide derivatives of terephtalic acid and testing for biological activity.
Synthesis of diamides of terephthalic acid consisted in reactions of aminoacids with terephthalic acid chloride1). Synthesis of dithioamide derivatives consisted in thionation2).
The compounds were tested for their antibacterial3), antifungal4) and antimycobacterial3) activities.
Results and discussion
The chemical structure of the received compounds, oxygen (1a-3a) and sulphur (1b-3b) analogs, was confirmed using 1H spectra and 13C NMR, and mass spectrometry.
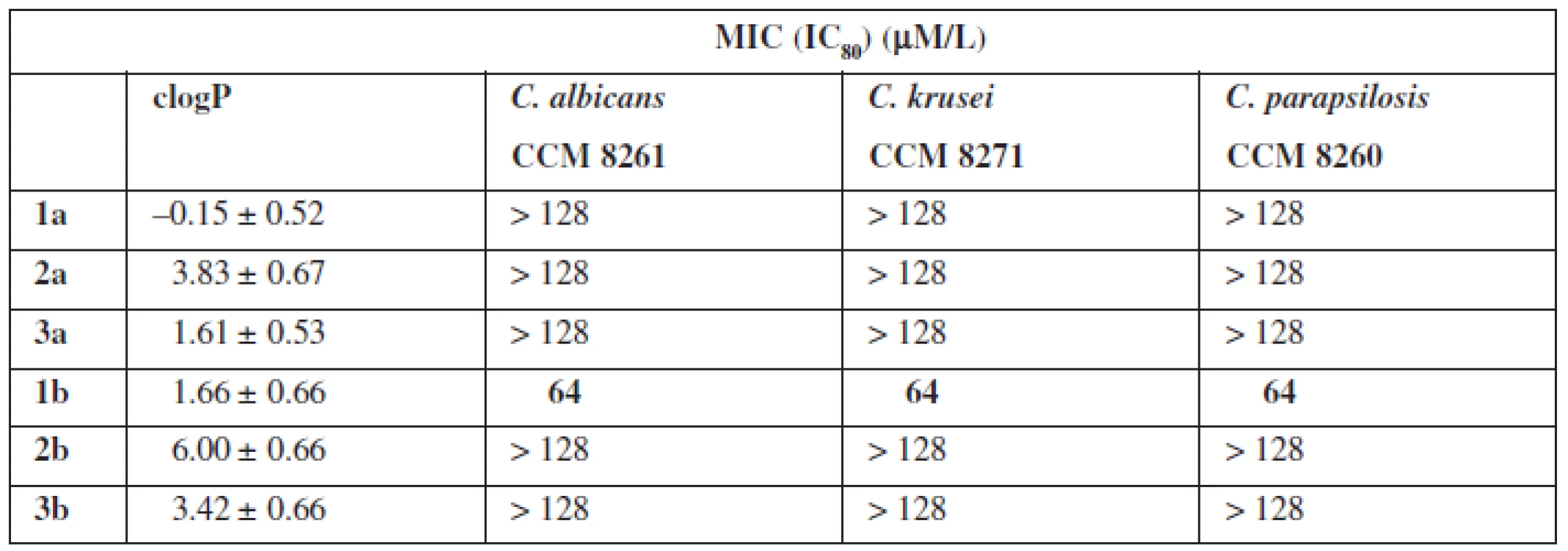
Setting a MIC (Minimal Inhibitory Concentration) parameter defined antifungal properties (Table 1). For the tests, three pathogenic species of the fungi species Candida (C. albicans, C. fragile, C. parapsolosis) were used.
The next stage of research was to determine the antimicrobial properties (Table 2). For this purpose the strains of Gram-positive bacteria S. aureus (Sa ATCC 29213), methicillin-resistant S. aureus (MRSA 63718, SA 630, SA 3202) and Gram-negative E. coli were used.
Tab. 2. Antibacterial activity 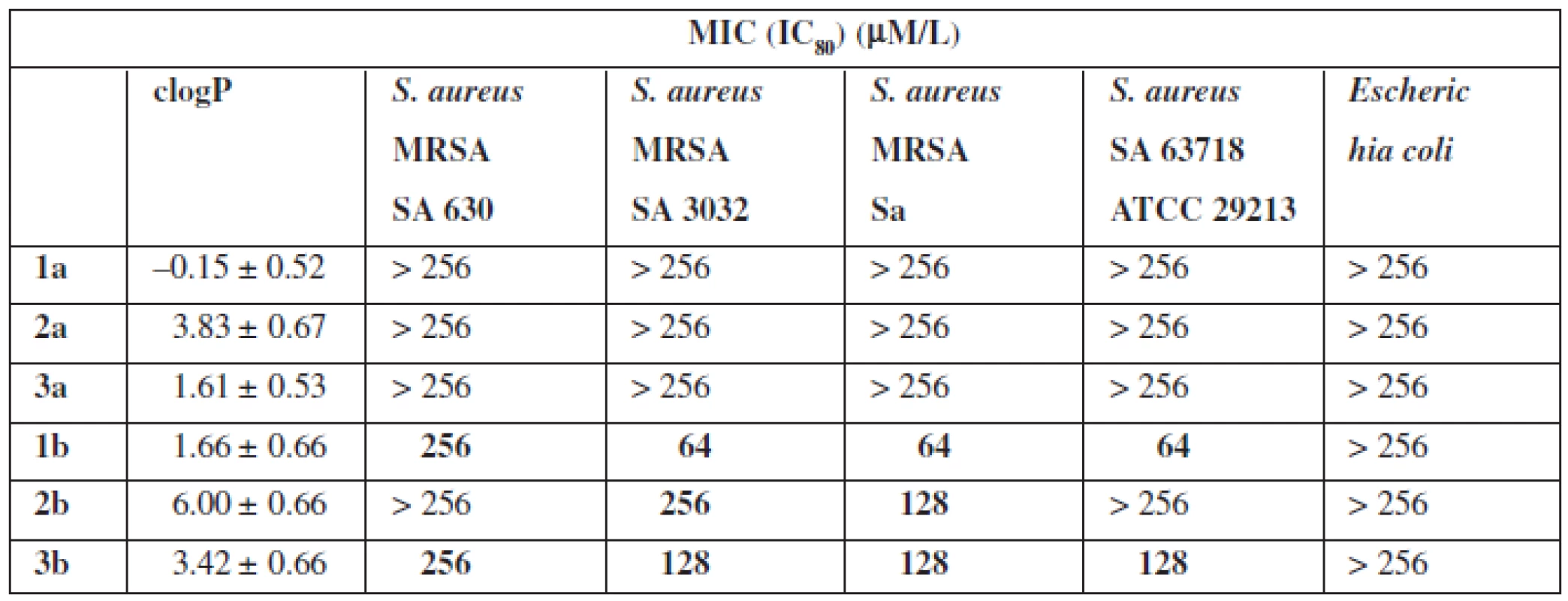
The final stage of biological research was to test the activity of bacteria species mycobacterium (Table 3). The tests were carried out using different incubation time, i. e. 3 to 21 days for the corresponding strain of bacteria.
Tab. 3. Antimycobacterial activity 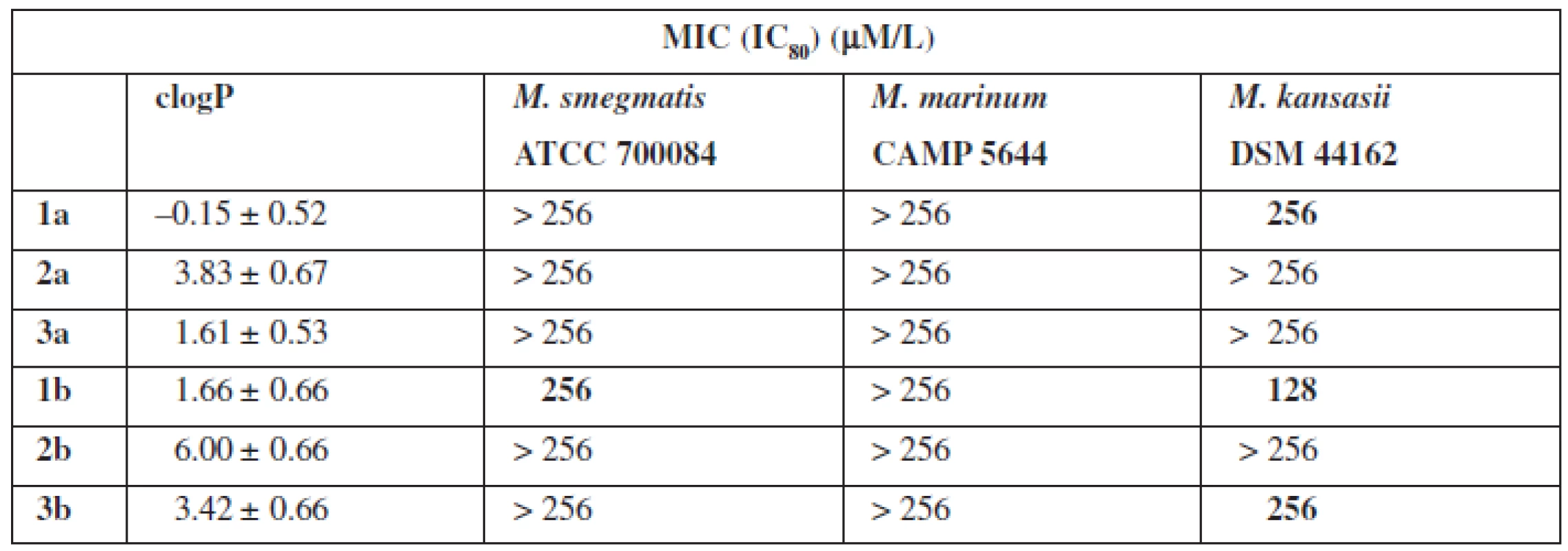
Conclusions
The tests of biological properties of new derivatives show an increase in activity for the thioamides in relation to their oxygen counterparts. However, none of the analogs tested showed high biological activity.
Mark Matussek is co-financed by the European Social Fund, the project DoktoRIS.
Conflicts of interest: none.
Mgr. Agnieszka Jędrzejowska
University of Silesia, Institute of Chemistry
Studencka 15/109 street, 40-743 Katowice, Poland
e-mail: a.jedrzejowska@o2.pl
Zdroje
1. Yu S-L., Doub X-Q., Qua D-H., Feng Ch-L. C2-symmetric benzene-based organogels: A rationally designed LMOG and its application in marine oil spill. J. Mol. Liq., 2014; 190, 94–98.
2. Polshettiwar V., Kaushik M. P. A new, efficient and simple method for the thionation of ketones to thioketones using P4S10/Al2O3. Tetrahedron Lett. 2004; 45, 6255–6257.
3. Pauk K., Zadrazilova I., Imramovsky A., Vinsova J., Pokorna M., Masarikova M., Cizek A., Jampilek J. New derivatives of salicylamides: Preparation and antimicrobial activity against various bacterial species. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2013; 21, 6574–6581.
4. Adlard P. A., Cherny R. A., Finkelstein D. I., Gautier E., Robb E., Cortes M., Volitakis I., Liu X., Smith J. P., Perez K., Laughton K., Li Q-X., Charman S. A., Nicolazzo J. A., Wilkins S., Deleva K., Lynch T., Kok G., Ritchie C. W., Tanzi R. E., Cappai R., Masters C. L., Barnham K. J., Bush A. I. Rapid Restoration of Cognition in Alzheimer’s Transgenic Mice with 8-Hydroxy Quinoline Analogs Is Associated with Decreased Interstitial ABβ, Neuron 2008; 59, 43–55.
Štítky
Farmacie Farmakologie
Článek vyšel v časopiseČeská a slovenská farmacie
Nejčtenější tento týden
2015 Číslo 6- Psilocybin je v Česku od 1. ledna 2026 schválený. Co to znamená v praxi?
- Nedůvěřivý pacient – tipy pro efektivní komunikaci v časové tísni
- Jak na přípravu keratolytik – cesta k technologicky zvládnutému přípravku
-
Všechny články tohoto čísla
- Antibakteriální účinky přírodních látek – silice
- Organická syntéza, Laboratórny manuál
- Cholinergický systém srdca
- Proběhl 42. mezinárodní kongres k dějinám farmacie
- Povrch těla a tělesná hmotnost dospělé české onkologické populace
- Stable gold nanoparticles – synthesis, bioconjugation and application
- Determination of antigripal drugs (pheniramine, phenylephrine) in biological samples by on-line CITP-CZE coupled with tandem mass spectrometry
- Development of the hydrocortisone butyrate qualitative determination method
- Estimation of lipohydrophilic properties of molecules with potential β3-agonistic activity
- Determination of the colorants in vitamin E by HPLC with photodiode array detection
- Analysis of flavonoids in grape leaves by HPLC-DAD-MS/MS
- Antioxidative protection of inactivated rabies vaccine with squalene adjuvant by β-carotene
- From an old drug to a new one: Synthesis of valproate from 5,5-dipropylbarbituric acid
- Synthesis and antimicrobial activity of novel sulfonamide derivatives
- Synthesis and antioxidant activity of phenylcarbamic acid derivatives acting on the cardiovascular system
- Synthesis and biological activity of selected cinnamic acid derivatives
- Synthesis and biological properties of chosen symmetrical amides and thioamides of terephthalic acid
- Synthesis of quinoline derivatives using a nano-Pd/Cu catalyst in the search of new fluorophores
- Synthesis of triclosan derivatives and their antimycobacterial effect
- The development of a dental drug in the form of medicated chewing gum
- Sympozia Sekce dějin farmacie ČFS v roce 2015
- Autorský rejstřík
- Česká a slovenská farmacie
- Archiv čísel
- Aktuální číslo
- Informace o časopisu
Nejčtenější v tomto čísle- Antibakteriální účinky přírodních látek – silice
- Povrch těla a tělesná hmotnost dospělé české onkologické populace
- Cholinergický systém srdca
- Organická syntéza, Laboratórny manuál
Kurzy
Zvyšte si kvalifikaci online z pohodlí domova
Současné možnosti léčby obezity
nový kurzAutoři: MUDr. Martin Hrubý
Všechny kurzyPřihlášení#ADS_BOTTOM_SCRIPTS#Zapomenuté hesloZadejte e-mailovou adresu, se kterou jste vytvářel(a) účet, budou Vám na ni zaslány informace k nastavení nového hesla.
- Vzdělávání